What is Scrum? Let’s find out.
Today we're going to dive into a popular Agile framework known as Scrum. Scrum is a highly effective framework for product development. Originating in the field of software development, Scrum has now spread its wings to diverse industries due to its ability to enhance teamwork, promote collective responsibility, and focus on delivering the highest value.

What is Scrum?
In its simplest form, Scrum is an Agile framework that facilitates team collaboration on complex tasks. It's a flexible product development strategy where a development team works as a unit to reach a common goal.
Scrum is most widely used in the realm of software development, but its principles and lessons can be applied to all types of teamwork. Scrum is part of the broader Agile mindset.
The agile mindset is based on 12 principles that emphasize flexibility, collaboration, customer feedback, and small, rapid iterations, as opposed to long drawn-out development cycles.
It advocates adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continuous improvement, and it encourages flexible responses to change. Scrum is a specific set of practices for applying the agile mindset.
Who is taking part in Scrum?
First, let’s talk about some key terms and concepts that make Scrum what it is. The Scrum team, a central component of the Scrum framework, is a collaborative unit comprised of the product owner, Scrum master, and development team, each playing a crucial role in successful product development.
The product owner is tasked with managing the product backlog, which lists all the product backlog items, and clarifying these to the team. But his role extends beyond that.
In fact, the Product Owner should be imbued with a clear product vision, and be responsible for putting together the product strategy. They should also maintain an active interest in the market and communicate extensively with customers/users, translating their needs into the product backlog. In this way, they feed back vital information to the team.
On the other hand, the Scrum Master is entrusted with helping with adherence to the Scrum framework and helping resolve any obstacles that may arise, his role lies in the effectiveness and ownership of the team and its coaching towards self-organization.
The development team in Scrum is responsible for turning the product backlog items into working increments of the product. It is a self-organizing and cross-functional group of individuals who have the necessary skills and expertise to deliver the product increment.
The team typically consists of developers, designers, testers, and any other roles required to complete the work.
One of the key principles of the development team in Scrum is its self-organization.
The team members collectively decide how to best accomplish the work, rather than being directed by a manager or external authority. This autonomy allows the team to adapt and respond to changes quickly, promoting creativity, ownership, and accountability.
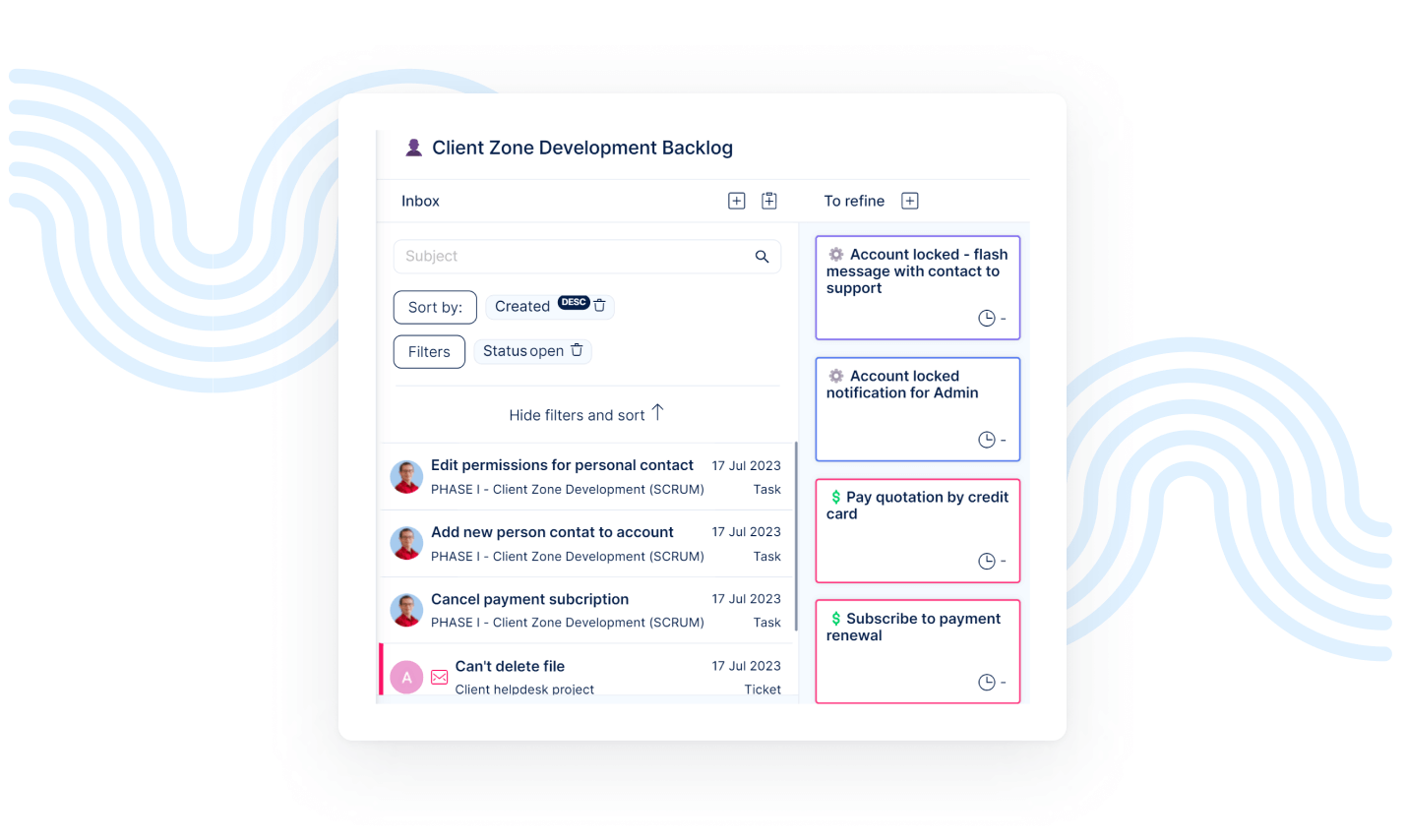
Scrum Boards backlog
How does it work?
In Scrum, a sprint is a fixed period (1-4 weeks) where specific product backlog items (PBI) are developed and delivered.
The team together with the PO creates the sprint goal and then the team commits to achieving it during the sprint planning meeting. The sprint goal provides a clear focus and direction for the development team's efforts during a sprint. It's in this meeting that they select particular Product Backlog Items (PBIs) that align with the goal. The velocity, which averages the work done by the team in each sprint is helping the team to select as many PBIs as the team is really able to finish within the sprint.
Each day during the sprint, the team shares a discussion about what is needed to be done to meet the sprint goal. This little planning of the day is called daily Scrum.
A process known as refinement is an ongoing activity where the team talks with the PO to align their understanding of the user need and agree on a possible solution (optionally the team also dedicates time to estimate the necessary efforts for each PBI). Usually, a separate meeting is done for this outside of planning. Regular refinement ensures clarity for future sprints.
The Definition of Done (DoD) establishes the criteria for when a product backlog item is considered complete. After each sprint, the work done and backlog are assessed in a Sprint review. The purpose of the review is to get feedback on the prepared work and adjust the plans or backlog items for the next sprint.
Retrospective identifies improvements for the next sprint or a few sprints ahead. It is very important that we don't repeat the same mistakes and work better/more efficiently. It's a practice of looking for places to improve our cooperation, ownership, and self-organization within the team and outside it.
The goal of this framework is continuous development and delivery of valuable increments of the product after each sprint to retrieve early feedback to demonstrate a small product increment to users (or their representatives) and determine whether the team is on the right track, and if the efforts genuinely meet users’ needs.
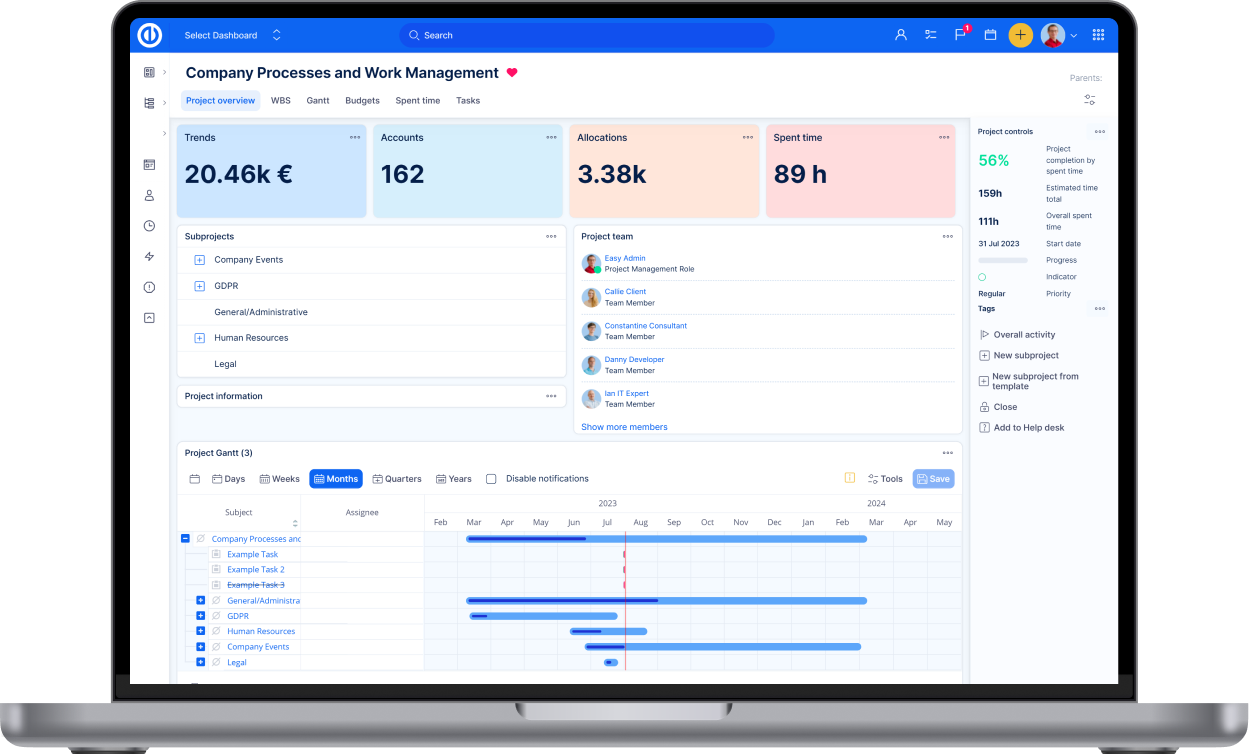
By leveraging these elements effectively, Scrum teams can enhance collaboration and deliver valuable increments of the product. For capturing this data you can use Scrum Boards.
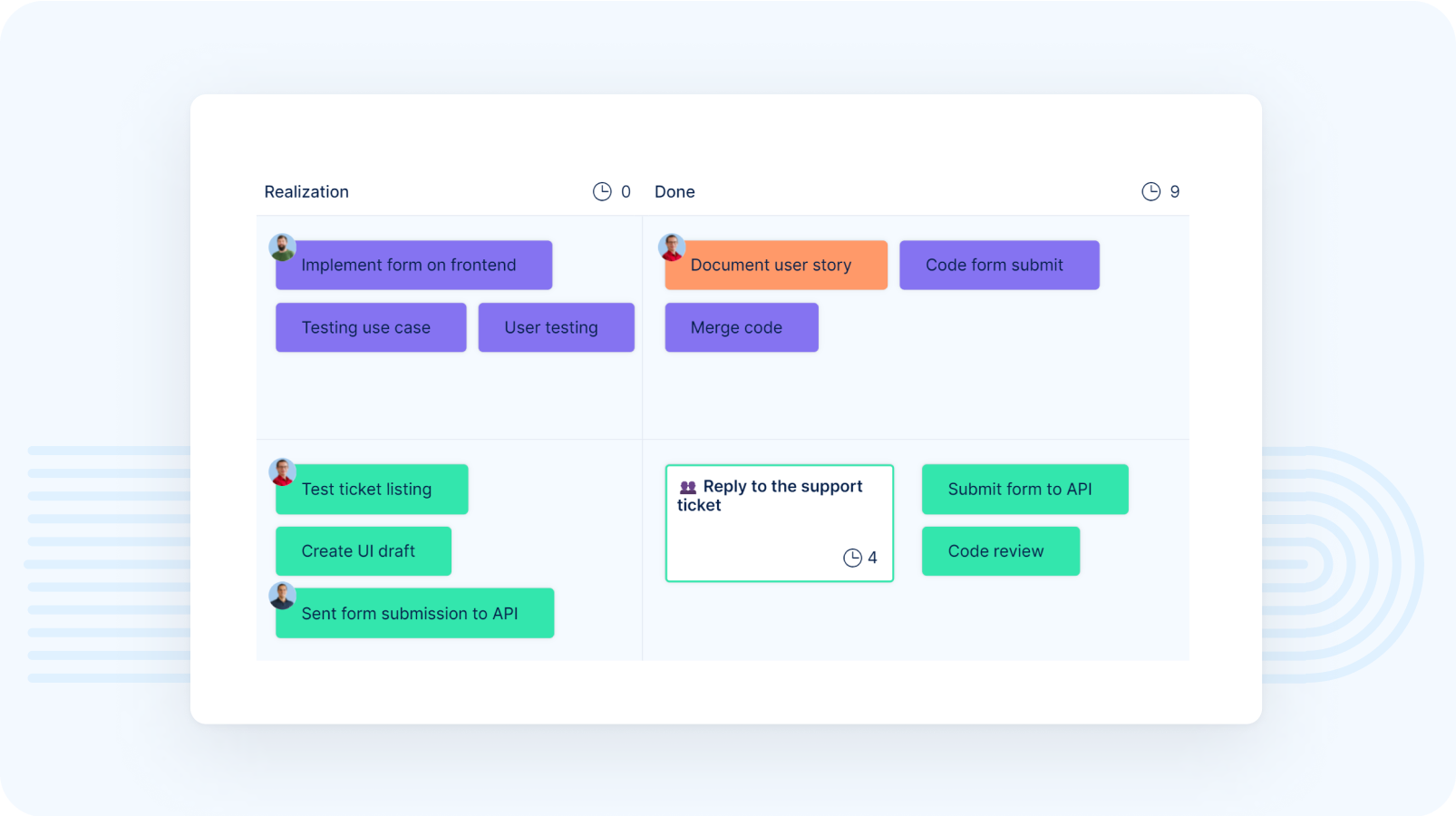
Scrum Boards planning
What are Scrum boards?
Scrum boards were originally created using paper and post-it notes, but in modern times of remote collaboration, you may encounter them mostly as an online tool. In order to organize your team effectively and transparently it is essential to choose a tool, which is as simple and transparent to everyone as working with slips of paper.
Why is Scrum so popular?
There are numerous reasons why many teams opt to use Scrum.
- Firstly, Scrum is renowned for increasing productivity. It accomplishes this by breaking down complicated tasks into more manageable pieces, making it easier for team members to handle them effectively and to get feedback earlier.
- On top of that, Scrum guarantees higher-quality outcomes through its regular checks and reviews with users/stakeholders.
- These systems ensure errors are identified early and corrected promptly.
- Lastly, Scrum bolsters team morale. It achieves this by promoting collaborative work and empowering the team to manage their work, which, in turn, fosters a more positive and conducive work environment.
Conclusion
Scrum is a framework that encourages team collaboration and delivers high-value products by breaking down complex tasks. It's no wonder that organizations worldwide are implementing Scrum to organize their work efficiently and successfully.
Whether you're thinking about implementing Scrum in your organization, a tool that can significantly enhance this experience is Easy Project 13. It comes equipped with all-new Scrum Boards approved by an expert from Scrum.org. If you aim to use Scrum, as it was intended to work, Easy Project can be a good starting point.
Easy Project Scrum Boards allow teams to seamlessly implement Scrum principles, boosting productivity, improving product quality, increasing stakeholder satisfaction, and nurturing a positive team environment. But most importantly - it promotes team collaboration.
With Easy Project 13, leveraging the power of Scrum becomes closer than ever.
Try the new Easy Project 13
Step up to the next level of project management. Try the new Easy Project 13 for free and experience the undisrupted flow of your projects and business operations.